Choosing the right PCB Materials is one of the most important decisions in the electronic product design process. Whether you’re working on a consumer device, an automotive control module, or a high-frequency RF system, the substrate you select directly impacts electrical performance, heat resistance, signal integrity, manufacturability, and long-term reliability. In the first 100 words alone, it becomes clear that the foundation of every printed circuit board relies not just on copper and components but on the core material beneath them. This article explains how different PCB substrates work, why their properties matter, and how to determine the best fit for your project.
- Understanding the Role of PCB Materials in Circuit Performance
- Types of PCB Materials and Their Unique Characteristics
- Dielectric Constant and Loss Tangent: Why They Matter When Choosing PCB Materials
- Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance in PCB Substrate Selection
- Mechanical Strength, Flexibility, and Dimensional Stability in PCB Materials
- Moisture Absorption and Environmental Reliability
- Cost Considerations When Choosing PCB Materials
- Case Study: How Material Choice Improved RF Performance in a Connectivity Device
- How to Match PCB Materials with Application Requirements
- Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Materials
- Conclusion: Choosing the Best PCB Materials for Your Project
Understanding the Role of PCB Materials in Circuit Performance
The substrate inside a printed circuit board does more than mechanically support copper traces. PCB Materials influence dielectric behavior, insulation strength, impedance control, and heat dissipation. As electronics become smaller, faster, and more thermally demanding, the substrate’s role becomes increasingly critical. According to IPC standards, material selection is a primary cause of PCB failure when overlooked during the design phase. Engineers must understand how resin systems, glass weave, and fillers interact to produce specific electrical and thermal characteristics.
High-quality substrates help stabilize signal transmission, prevent delamination, and maintain dimensional integrity during soldering. In contrast, lower-grade materials may warp, absorb moisture, or break down when exposed to thermal cycling. By understanding how each material behaves, designers can make smarter choices that reduce manufacturing costs and extend product lifespan.
Types of PCB Materials and Their Unique Characteristics
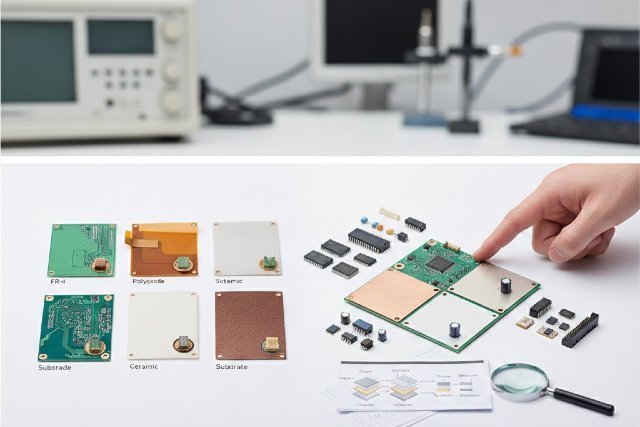
There are many substrate options available today, ranging from standard FR-4 laminates to advanced PTFE composites used in aerospace and 5G systems. Each material has unique mechanical and electrical properties that influence how a circuit performs. The most widely used substrate is FR-4, a fiberglass-epoxy laminate known for its balance of durability, affordability, and dielectric performance. FR-4 suits everyday applications such as consumer devices, IoT modules, power supplies, and automotive electronics. Its dielectric constant, typically between 4.1 and 4.7, makes it stable enough for controlled impedance applications without excessive cost.
At the higher end of performance are ceramic-based PCB Materials designed for extreme heat and high-frequency operation. These materials offer exceptional thermal conductivity and low dielectric loss, making them ideal for radar systems, satellite hardware, and high-power LEDs. Their superior stability allows circuits to function reliably in harsh environments where conventional FR-4 would degrade or deform.
Engineers working on RF or microwave designs often turn to PTFE (Teflon) substrates, which offer extremely low dielectric constants and minimal signal loss. PTFE-based laminates like Rogers RT/duroid are widely used in high-frequency antennas, phased-array networks, and 5G infrastructure. The challenge with PTFE materials is manufacturability, as their softness requires more precise drilling and lamination processes.
Metal-core substrates represent another important category. These substrates incorporate aluminum or copper cores to help dissipate heat quickly away from high-power components. LED lighting, power converters, and battery management systems often rely on metal-core PCBs to maintain thermal stability. The choice between aluminum and copper depends on conductivity, weight, and application-specific constraints.
Dielectric Constant and Loss Tangent: Why They Matter When Choosing PCB Materials
Electrical performance depends heavily on two essential properties: dielectric constant (Dk) and loss tangent (Df). The dielectric constant determines how quickly signals travel through a substrate, while loss tangent measures how much signal energy dissipates as heat. Lower values are ideal for high-speed digital or RF systems because they help maintain signal integrity.
FR-4 offers reasonable Dk values for mid-range performance applications, but materials like PTFE, hydrocarbon ceramics, and advanced laminates deliver significantly better results for high-frequency designs. For example, Rogers 4350B has a Dk of around 3.66 and a very low loss tangent, making it ideal for antennas and filters. Researchers at IEEE have shown that the choice of substrate can reduce signal attenuation by more than 40 percent in certain microwave applications. This demonstrates why selecting materials based on electrical parameters rather than cost alone is essential.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance in PCB Substrate Selection
Thermal performance is another key factor when evaluating PCB Materials. Electronics generate heat, and without proper substrate selection, temperature spikes can cause delamination, cracking, or copper peel-off. The glass transition temperature (Tg) determines how well a substrate withstands heat during soldering and operation. Standard FR-4 materials typically have Tg values around 130°C to 150°C, while high-Tg FR-4 can exceed 180°C.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial automation often require high-temperature materials due to harsh operating conditions. Ceramic substrates provide exceptional thermal stability, while metal-core PCBs help dissipate heat quickly. Studies published by IPC indicate that thermal stress is a leading cause of PCB field failures, especially in power electronics. Choosing a substrate with a high decomposition temperature (Td) helps ensure long-term reliability.
Mechanical Strength, Flexibility, and Dimensional Stability in PCB Materials
The physical strength of a substrate influences how well a PCB resists vibration, bending, and manufacturing stress. Rigid materials like FR-4 are ideal for traditional board designs, while flexible polyimide substrates are used in foldable, wearable, or compact devices. Flex PCBs can bend without cracking and are commonly found in smartphones, medical sensors, and automotive instrument clusters.
Dimensional stability matters because even small expansions or contractions can affect alignment during manufacturing. Materials with low thermal expansion coefficients maintain their shape better during solder reflow or exposure to environmental changes. High-density interconnect (HDI) designs, which use microvias and fine-pitch features, require materials with superior dimensional stability to ensure drill accuracy and impedance consistency.
Moisture Absorption and Environmental Reliability
Some substrates absorb moisture more easily than others. High moisture absorption can lead to dielectric shifts, swelling, and delamination during reflow soldering. FR-4 materials have moderate moisture absorption, while PTFE and polyimide absorb significantly less. If a product will be used outdoors or in humid environments, low-moisture substrates are essential for maintaining performance.
Environmental reliability also depends on chemical resistance, UV stability, and long-term aging. Applications exposed to oils, fuels, or corrosive chemicals often require specialized laminates with protective coatings or enhanced resin systems. Ensuring that your material meets IPC-4101 standards can help reduce risks associated with environmental exposure.
Cost Considerations When Choosing PCB Materials
Cost plays a major role in substrate selection, especially for large-scale manufacturing. FR-4 remains the most economical choice due to widespread availability and ease of processing. However, advanced materials such as PTFE or ceramic substrates can significantly increase production costs. Engineers must balance performance requirements with budget constraints, ensuring that the chosen material aligns with product goals.
A useful strategy is to categorize requirements based on essential versus optional features. For example, if high-frequency performance is critical, investing in low-loss materials may save costs later by reducing failures or performance issues. Conversely, for low-speed consumer electronics, standard FR-4 may offer the best balance.
Case Study: How Material Choice Improved RF Performance in a Connectivity Device
A wireless device manufacturer experienced inconsistent antenna performance in cold environments. Testing revealed that the standard FR-4 substrate introduced variability in dielectric constant under temperature changes. By switching to a low-loss hydrocarbon ceramic laminate, the company reduced signal drift and improved range reliability by nearly 30 percent. This example illustrates how selecting the right PCB Materials can resolve complex engineering challenges that may not be obvious during early prototyping.
How to Match PCB Materials with Application Requirements
The ideal substrate depends on your application’s electrical, thermal, and mechanical needs. High-speed routers, 5G antennas, and RF amplifiers require materials with low Dk, low loss tangent, and stable high-frequency behavior. Power electronics demand substrates with high thermal conductivity and strong insulation. Wearables and compact devices benefit from flexible substrates that allow creative form factors.
Matching the material to your application involves understanding not only current requirements but potential product evolutions. If future updates may require higher frequencies or increased power, choosing a more advanced substrate early on can save development time and redesign costs.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Materials
What are the most common PCB Materials?
The most common materials include FR-4, PTFE laminates, polyimide, ceramic substrates, and metal-core laminates. Each serves a different performance requirement.
Which substrate is best for high-frequency designs?
PTFE, hydrocarbon-ceramic laminates, and low-loss materials like Rogers 4000 series are preferred for RF and microwave applications due to low dielectric loss.
Can I use FR-4 for high-speed digital circuits?
Standard FR-4 works for many mid-range speeds, but high-speed systems may require enhanced FR-4 or low-loss laminates to maintain signal integrity.
Are flexible PCB Materials durable?
Yes. Polyimide-based flex circuits are extremely durable and can withstand bending cycles, heat, and vibration better than many rigid substrates.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best PCB Materials for Your Project
Selecting the right PCB Materials requires a balance of electrical performance, thermal stability, mechanical strength, and cost. By understanding dielectric behavior, heat resistance, environmental reliability, and application-specific needs, engineers can choose substrates that ensure long-term performance and manufacturability. The right material elevates circuit reliability, reduces field failures, and aligns your design with industry standards. Making an informed choice today ensures that your product performs consistently from prototype to mass production.