In today’s cloud-driven world, enterprises are rapidly shifting away from hardware-heavy network infrastructures toward more agile, subscription-based models. Network as a Service (NaaS) is leading this transformation by replacing traditional network ownership with on-demand, scalable, and centrally managed network delivery. Within the first hundred words, it becomes clear that Network as a Service is not a trend — it’s a strategic necessity. Organizations facing hybrid work, edge computing, global expansion, and rising cybersecurity demands are embracing NaaS for its flexibility, automation, and cost-efficiency.
- What Is Network as a Service? A Clear, Modern Definition
- Why Network as a Service Is Transforming Enterprise Connectivity
- The Core Technologies Powering Network as a Service
- Real-World Example: How Enterprises Use Network as a Service
- Key Benefits of Network as a Service for Modern Enterprises
- Market Trends Driving NaaS Adoption
- Challenges and Considerations Before Adopting Network as a Service
- FAQ: Quick Answers Optimized for Featured Snippets
- Conclusion: Why Network as a Service Is the Future of Enterprise Connectivity
As digital transformation accelerates, companies need networking capabilities that evolve as quickly as their business models. NaaS provides exactly that: adaptable, cloud-native networking built for modern enterprises.
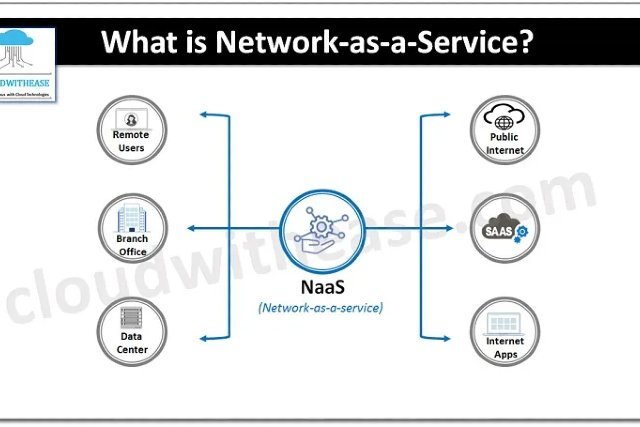
What Is Network as a Service? A Clear, Modern Definition
Network as a Service is a cloud-based model where enterprises consume networking functions — like bandwidth, routing, firewalls, SD-WAN, or Wi-Fi — on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. Instead of purchasing equipment, organizations access a fully managed network infrastructure delivered as a service.
This approach mirrors the philosophy of SaaS, IaaS, and other cloud services but applies it to enterprise networking. In practice, NaaS providers handle deployment, optimization, maintenance, monitoring, and security, allowing IT teams to focus on strategy — not hardware.
According to Gartner, by 2026, 50% of new enterprise network deployments will use NaaS, demonstrating how quickly enterprises are shifting away from traditional network architectures.
Why Network as a Service Is Transforming Enterprise Connectivity
NaaS introduces a level of speed, transparency, and adaptability that traditional networks cannot match. Companies adopting NaaS experience a measurable impact on cost structure, operational flexibility, and security posture.
Agility for Cloud, Hybrid, and Remote Work
As distributed work becomes the norm, centralized hardware-based networks struggle to keep up. NaaS enables remote offices and hybrid teams to access secure, optimized connectivity without the slow deployment cycles of legacy networks.
Scalable Bandwidth and Resources on Demand
Enterprises can instantly scale bandwidth based on seasonal demand, business expansion, or workload spikes. Instead of relying on physical upgrades, adjustments happen through cloud dashboards with zero downtime.
Improved Security Through Centralized Policies
NaaS integrates Zero Trust, AI-driven threat detection, and automated patching. With centralized control, businesses reduce the risk of configuration errors — one of the leading causes of network breaches.
Predictable Costs and Reduced CAPEX
Instead of large upfront investments in routers, switches, and firewalls, companies shift to predictable OPEX models. This is especially beneficial for startups, global enterprises, and organizations undergoing rapid growth.
The Core Technologies Powering Network as a Service
NaaS represents a convergence of cloud computing, automation, and security innovation. Several key technologies make Network as a Service both effective and future-proof.
SD-WAN: The Backbone of Modern Enterprise Networks
SD-WAN improves application performance by intelligently routing traffic across the best available links. Most NaaS providers build SD-WAN into their offerings to deliver fast, reliable connectivity across multiple sites.
SASE and Zero Trust Architecture
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) merges networking and security in the cloud, providing identity-based access control and continuous device validation. This ensures users and devices receive the same security level regardless of location.
AI and ML-Powered Network Automation
Through AI-driven analytics, NaaS platforms automatically optimize performance, detect anomalies, and adjust configurations. This reduces the need for manual oversight and speeds up troubleshooting.
Edge Computing Integration
With edge workloads growing, NaaS extends network capabilities directly to distributed environments, ensuring low-latency performance for IoT, automation, and real-time analytics.
Real-World Example: How Enterprises Use Network as a Service
Imagine a global retail chain opening 50 new stores in six months. Traditionally, each store would require manual network setup, hardware provisioning, and onsite technical support. With Network as a Service, the IT team simply configures network templates in the cloud and deploys plug-and-play devices shipped directly to stores.
The result is immediate connectivity, consistent security policies, and centralized monitoring — dramatically reducing setup time and operational overhead.
This model is especially valuable in industries such as:
Financial services
Healthcare
Manufacturing
Hospitality
Logistics
Education
Each sector benefits from simplified deployment, regulated security controls, and real-time observability.
Key Benefits of Network as a Service for Modern Enterprises
Faster Time to Deployment
With pre-configured templates and automated provisioning, networks can be deployed in minutes rather than weeks.
Enhanced Network Visibility and Control
NaaS platforms provide unified dashboards showing traffic patterns, device health, and security threats in real time.
Consistent Global Connectivity
Whether connecting a remote worker, branch office, or cloud environment, NaaS ensures uniform performance and policy enforcement.
Sustainability Through Reduced Hardware Waste
Enterprises buy fewer physical devices and extend the lifecycle of network hardware through cloud-based functions.
Market Trends Driving NaaS Adoption
The Rise of Hybrid Work
40% of knowledge workers now operate remotely at least part-time.
This shift demands scalable, secure, cloud-delivered network access.
Cloud Migration Across All Industries
As enterprises move workloads to AWS, Azure, and GCP, networking must evolve to support multi-cloud performance, visibility, and security.
Cybersecurity Pressures
With cyberattacks increasing 38% year over year (Check Point Research), NaaS models with built-in Zero Trust are becoming essential.
Demand for Predictable IT Spending
Subscription-based networking aligns well with modern financial planning strategies.
Challenges and Considerations Before Adopting Network as a Service
Network as a Service is powerful, but it isn’t a universal solution. Companies should carefully evaluate:
Vendor Lock-In Risks
Some NaaS platforms may require proprietary tools, reducing flexibility over time.
Data Residency and Compliance Requirements
Enterprises operating in regulated sectors — such as healthcare or finance — must ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and regional data laws.
Migration Complexity
Transitioning from legacy infrastructure to cloud-based networking requires planning and may need hybrid models during the shift.
Performance SLAs
Not all NaaS providers offer the same quality of experience. Choosing one with strong SLAs is critical.
FAQ: Quick Answers Optimized for Featured Snippets
What is Network as a Service?
Network as a Service is a cloud-based model where enterprises consume network functions on a subscription basis instead of owning physical infrastructure.
How does Network as a Service work?
NaaS providers deliver scalable bandwidth, routing, security, and connectivity through the cloud, allowing centralized management and automation.
What are the benefits of Network as a Service?
NaaS offers reduced costs, faster deployment, improved security, and flexible scalability.
Is Network as a Service secure?
Yes. Most NaaS solutions include Zero Trust, SASE, encryption, and continuous monitoring for enhanced protection.
Who should use Network as a Service?
Organizations with distributed workforces, multiple branch locations, or cloud-heavy environments benefit most from NaaS.
Conclusion: Why Network as a Service Is the Future of Enterprise Connectivity
As businesses continue moving toward cloud-first operations, Network as a Service delivers the flexibility, scalability, and intelligence required to stay competitive. By shifting from hardware-centric models to service-based architectures, enterprises gain faster deployments, stronger security, predictable costs, and a network that evolves with their digital strategy. Network as a Service is more than a new technology — it is a foundational shift in how organizations build and manage global connectivity. Its adoption signals a future where networks are dynamic, automated, and designed to support the rapid pace of modern innovation.